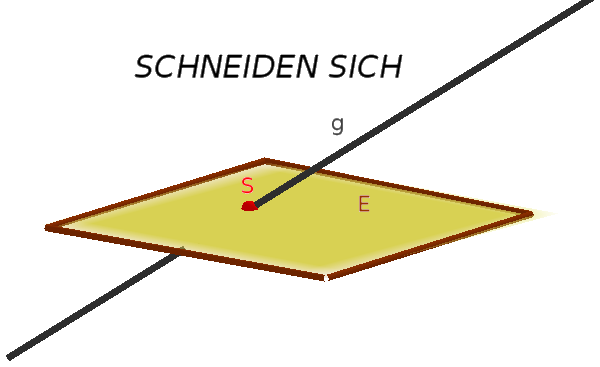
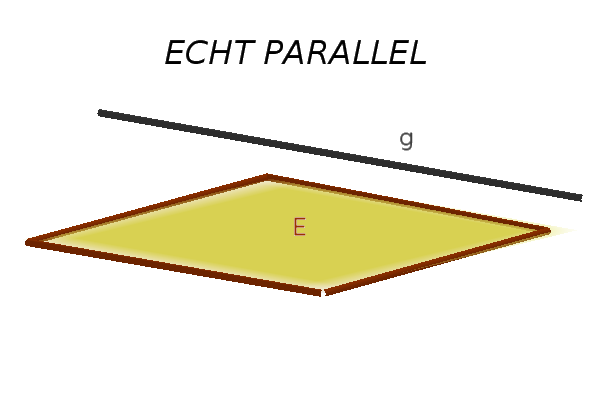
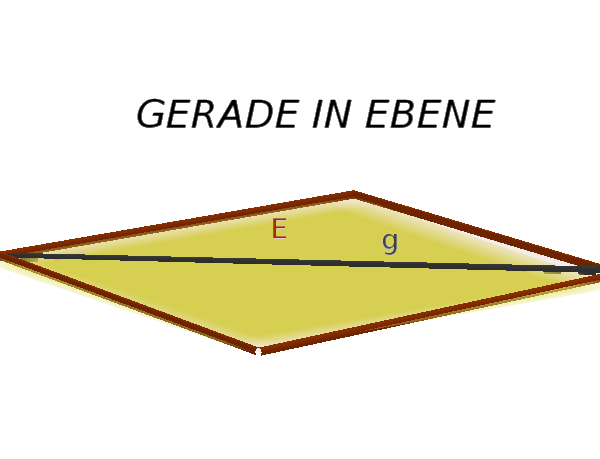
Man unterscheidet drei mögliche Lagebeziehungen zwischen einer Geraden $g$ und einer Ebene $E$.



$\text{g: } \vec{x} = \begin{pmatrix} 2 \\ 1 \\ 1 \end{pmatrix} + r \cdot \begin{pmatrix} 2 \\ -3 \\ 4 \end{pmatrix}$
$\text{E: } 2x+y+2z=-2$
$\begin{pmatrix} x \\ y \\ z \end{pmatrix} = \begin{pmatrix} 2 \\ 1 \\ 1 \end{pmatrix} + r \cdot \begin{pmatrix} 2 \\ -3 \\ 4 \end{pmatrix}$
Jede Zeile entspricht einer Gleichung
$\text{E: } 2\color{red}{x}+\color{blue}{y}+2\color{green}{z}=-2$
$2\cdot\color{red}{(2+2r)}$ $+\color{blue}{(1-3r)}$ $+2\cdot\color{green}{(1+4r)}$ $=-2$
Nun werden die Klammern aufgelöst und die Gleichung nach $r$ umgestellt
$4+4r+1-3r+2+8r$ $=-2$
$7+9r=-2\quad|-7$
$9r=-9\quad|:9$
$r=-1$
=> Gerade $g$ und Ebene $E$ schneiden sich.
Der Schnittpunkt wrid berechnet, indem man $r=-1$ in die Geradengleichung einsetzt.
$\begin{pmatrix} 2 \\ 1 \\ 1 \end{pmatrix} + (-1) \cdot \begin{pmatrix} 2 \\ -3 \\ 4 \end{pmatrix}$ $=\begin{pmatrix} 0 \\ 4 \\ -3 \end{pmatrix}$
=> Schnittpunkt $S(0|4|-3)$.